Accounting is the art of recording, classifying and summarizing, in a significant manner, and in terms of money, transactions and events which are, in part at least of a financial character, and interpreting the results thereof.
Accounting is the science of
recording and classifying business transactions and events, primarily of a
financial character, and the art of making significant summaries,
analysis and interpretations of these transactions and events and communicating
the result to persons who must make decisions or form judgments. - Herold Bierman and Allan R. Drebin
Accounting may be defined as the
process of collecting, recording, summarizing and communicating financial
information.
Accounting refers to the
system involved in making a financial record of business transactions and in
the preparation of statements concerning the assets, liabilities, capital and
operating results of the business.
Accounting is nothing but a
means of communicating the results of business operations to varies parties
interested in or connected with the business, viz., the owner, creditors,
investors, government, financial institutions and other agencies. Accounting is,
therefore, rightly called as the language of business.
The basis purpose of a
language is to serve as a means of communication. Accounting also serves this
purpose. Accounting is not only associated with business but also with every
body who is interested in keeping an account for the money received and money
spent.
basis purpose of a language is to serve as a means of communication. Accounting also serves this purpose. Accounting is not only associated with business but also with every body who is interested in keeping an account for the money received and money spent.
Nature of Accounting:- The
analysis of the above definitions brings out the following as attributes of
accounting:
- It is the art of recording and
classifying business transactions and events.
- The events and transactions of
a financial nature must be recorded in monetary terms, while the events
and transactions of a non-financial nature cannot be recorded.
- The record should reflect the
importance of the transactions so recorded both individually and
collectively, which includes summarization, thereby making it amenable to
analysis.
- The users of the financial
statements should be able to obtain the message encompassed in such
financial statements, and it is the knowledge of accounting, which enables
the user to understand the contents of the financial statements.
Objectives
of Accounting
·
As
an information system, the basic objective of accounting is to provide useful
information to the interested group of users, both external and internal. The
necessary information, particularly in case of external users, is provided in
the form of financial statements, viz., profit and loss account and balance
sheet.
·
Besides
these, the management is provided with additional information from time to time
from the accounting records of business.
The primary objectives of accounting include the following:
- Maintaining
Accounting Records
- Ascertainment
of Profit or Loss
- Ascertainment
of Financial Position
- Communication
of Information
Scope of Accounting:- Accounting plays a
key role in serving a systematic and up-to-date record of varied and numerous
business transactions. Its target is to analyse the financial transactions as
they take place, to record them in orderly fashion, to group and arrange the information
in terms of useful and understandable financial report (Balance Sheet, Income
Statement) and to assist in the process of interpretation.
Accounting is a service activity. Its function is to
provide quantitative information, primarily financial in nature, about economic
entities that is useful in making economic decisions, in making reasoned
choices among alternative course of action.
Accounting is thus not
an end itself but a means to an end. It is mainly a service function. In broad
perspective an accounting system should concern itself with the following
information:
- Analysis of past financial data
to find out the reasons for bad condition of the concern and corrective
measures for improvement of the business.
- Accounting is an art, on the
other hand, it is the application of knowledge comprising of some accepted
theories, rules, concepts and conventions. It helps us to achieve our
goals and tells us the manner in which we may attain our objectives in the
best possible way. The more we practice an art the more expert we become
in it.
- Accounting is a science because
recording, classifying and summarising of business transactions is done on
the basis of certain principles of double entry system which are
universally applicable.
- Accounting seems to be very
important in financial forecasting and financial forecasting helps in
estimating the profitable projects and out of these profitable projects
accountant chooses the one which is more profitable for the concern.
- For decision-making accounting
is useful. Accounting helps the accountants to take decision about capital
structures, cost of capital, an ideal capital gearing ratio, capital
budgeting, working capital, cash, budget, cost control, inventory
management etc.
- Accounting is a technique which
compares the cost of various departments and thus find out which
department is efficient than the other.
- As is common with physicians,
engineers, lawyers, and architects, accountants (including CPAs) commonly
are engaged in professional practice or are employed by business,
government entities, non-profit organisations and so on.
Accounting can be
classified into the following categories:
Ø Financial accounting
Ø Management accounting (including Cost
accounting
Ø Auditing
Ø Others like Price level changes accounting,
Social cost accounting, Social auditing, Human resource accounting, Forensic
accounting, Creative accounting, Value added accounting etc.
Book keeping
Recording of financial transactions in a proper manner related to the business operation of an entity is known as book- keeping. Book -keeping is the permanent recording of financial transactions in a proper manner in the books of accounts of an entity so that their financial effect on the business of entity can be seen. There is a difference between the two terms bookkeeping and accounting.
Book-keeping and accounting are different from each other. Bookkeeping is an important part of accounting. Accounting is broader than book-keeping. Accounting includes a design of accounting systems which book-keepers use for the preparation of financial statements, audits, cost studies, income-tax statements etc.
There is a difference between the two terms bookkeeping and accounting, let us understand what is bookkeeping and accounting, their processes and difference between the two. While doing Bookkeeping, we need to follow the basic accounting concepts and accounting conventions.
Bookkeeping is clerical in nature. Book-keeping is usually done by junior employees of the entity. Most of the entities nowadays use computers for bookkeeping rather than recording them manually. Accounting of an entity depends on its book-keeping system.
Book-keeping is the basis for accounting. It is because it is responsible for the proper recording of financial transactions. Whereas, Accounting involves classification, summarizing and reporting of financial transactions. It involves the preparation of source documents for all the financial transactions of the entity.
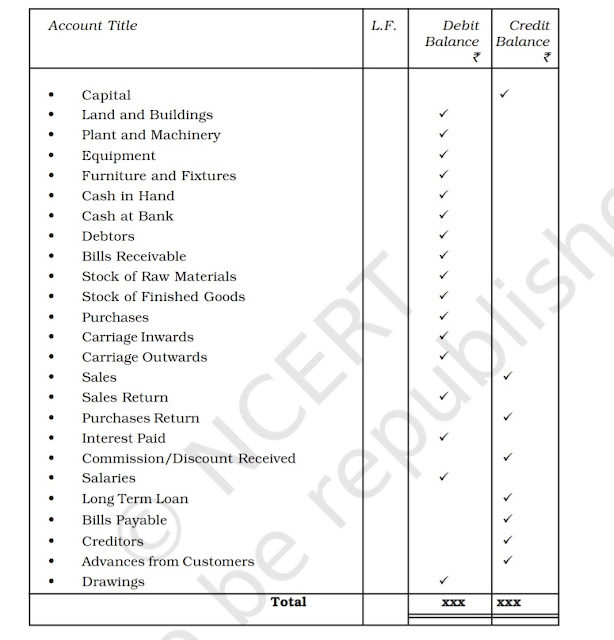
LEDGER
All
the accounts identified on the basis of transactions recorded in different journals/books
such as Cash Book, Purchase Book, Sales Book etc. will be opened and maintained
in a separate book called Ledger. So a ledger is a book of account; in which
all types of accounts relating to assets, liabilities, capital, expenses and
revenues are maintained. It is a complete set of accounts of a business
enterprise.
Thus, from the various journals/Books of a business enterprise, all transactions recorded throughout the accounting year are placed in relevant accounts in the ledger through the process of posting of transactions in the ledger. Thus, posting is the process of transfer of entries from Journal/Special Journal Books to ledger.
Features of ledger:-
- Ledger
is an account book that contains various accounts to which various business
transactions of a business enterprise are posted.
- It
is a book of final entry because the transactions that are first entered in the
journal or special purpose Books are finally posted in the ledger. It is also
called the Principal Book of Accounts.
- In
the ledger all types of accounts relating to assets, liabilities, capital, revenue
and expenses are maintained.
- It
is a permanent record of business transactions classified into relevant accounts.
- It
is the ‘reference book of accounting system and is used to classify and
summarise transactions to facilitate the preparation of financial statements.
Importance of Ledger:- Ledger is an important book of Account. It contains all the accounts in which all the business transactions of a business enterprise are classified. At the end of the accounting period, each account will contain the entire information of all the transactions relating to it. Following are the advantages of ledger.
Knowledge of Business results:- Ledger provides detailed information about revenues and expenses at one place. While finding out business results the revenue and expenses are matched with each other.
· Knowledge of book value of assets:- Ledger records
every asset separately. Hence, you can get the information about the Book value
of any asset whenever you need.
· Useful for management:- The information
given in different ledger accounts will help the management in preparing
budgets. It also helps the management in keeping the check on the performance
of business it is managing.
· Knowledge of Financial Position:- Ledger provides
information about assets and liabilities of the business. From this we can
judge the financial position and health of the business.
· Instant Information:- The business
always need to know what it owes to others and what the others owe to it. The
ledger accounts provide this information at a glance through the account
receivables and payables.
What Is a
Budget?
A budget is an
estimation of revenue and expenses over a specified future
period of time and is usually compiled and re-evaluated on a periodic basis. Budgets can
be made for a person, a group of people, a business, a government, or just
about anything else that makes and spends money.
To manage your
monthly expenses, prepare for life's unpredictable events, and be able to
afford big-ticket items without going into debt, budgeting is important.
Keeping track of how much you earn and spend doesn't have to be drudgery,
doesn't require you to be good at math, and doesn't mean you can't buy the
things you want. It just means that you'll know where your money goes, you'll
have greater control over your finances.
Understanding Budgeting:- A budget is a microeconomic
concept that shows the trade-off made when one good is exchanged for another.
In terms of the bottom line—or the end result of this trade-off—a surplus
budget means profits are anticipated, a balanced budget means
revenues are expected to equal expenses, and a deficit budget means
expenses will exceed revenues.
What are Financial
Statements :- Financial statements are
a collection of summary-level reports about an organization's financial
results, financial position, and cash flows. They include the income statement,
balance sheet, and statement of cash flows.
Advantages of Financial
Statements:- Financial Statements are
useful for the following reasons:
Ø
To
determine the ability of a business to generate cash, and the sources and uses
of that cash.
Ø
To
determine whether a business has the capability to pay back its debts.
Ø
To
track financial results on a trend line to spot any looming profitability
issues.
Ø
To
derive financial ratios from the statements that can indicate the condition of
the business.
Ø
To
investigate the details of certain business transactions, as outlined in the
disclosures that accompany the statements.
Ø
To
use as the basis for an annual report, which is distributed to a company’s
investors and the investment community.
Disadvantages of
Financial Statements:-
There are few downsides
to issuing financial statements. A possible concern is that they can be
fraudulently manipulated, leading investors to believe that the issuing entity
has produced better results than was really the case. Such manipulation can
also lead a lender to issue debt to a business that cannot realistically repay
it.
Balance Sheet:-
The term balance sheet refers to a financial
statement that reports a company's assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity
at a specific point in time. Balance sheets provide the basis for computing
rates of return for investors and evaluating a company's capital structure. In short, the balance sheet is a financial statement that provides a snapshot of what a
company owns and owes, as well as the amount invested by shareholders. Balance
sheets can be used with other important financial statements to conduct
fundamental analysis or calculating financial ratios.
The balance sheet adheres to the
following accounting equation, with assets on one side, and liabilities plus
shareholder equity on the other, balance out:
Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders' Equity
This formula is intuitive. That's
because a company has to pay for all the things it owns (assets) by either
borrowing money (taking on liabilities) or taking it from investors (issuing
shareholder equity)
Components of a Balance Sheet:-
Assets:- Accounts within this segment are listed from top to
bottom in order of their liquidity. This is the ease with which
they can be converted into cash. They are divided into current assets, which
can be converted to cash in one year or less; and non-current or long-term
assets, which cannot.
Here is the general
order of accounts within current assets:
- Cash and
cash equivalents are the most liquid assets and can include Treasury
bills and short-term certificates of deposit, as well as hard currency.
- Marketable
securities are equity and debt securities for which there is a liquid
market.
- Accounts
receivable (AR) refer to money that customers owe the company. This
may include an allowance for doubtful accounts as some customers may not
pay what they owe.
- Inventory
refers to any goods available for sale, valued at the lower of the cost or
market price.
- Prepaid expenses represent the value that has already been paid for, such as insurance, advertising contracts, or rent.
Long-term assets
include the following:
- Long-term
investments are securities that will not or cannot be liquidated in the
next year.
- Fixed
assets include land, machinery, equipment, buildings, and other
durable, generally capital-intensive assets.
- Intangible
assets include non-physical (but still valuable) assets such as
intellectual property and goodwill. These assets are generally only listed
on the balance sheet if they are acquired, rather than developed in-house.
Their value may thus be wildly understated (by not including a globally
recognized logo, for example) or just as wildly overstated.
Liabilities:- A liability is any money that a
company owes to outside parties, from bills it has to pay to suppliers to
interest on bonds issued to creditors to
rent, utilities and salaries. Current liabilities are due within one year and
are listed in order of their due date. Long-term liabilities, on the other
hand, are due at any point after one year.
Current liabilities accounts
might include:
- current
portion of long-term debt
- bank
indebtedness
- interest
payable
- wages
payable
- customer
prepayments
- dividends
payable and others
- earned
and unearned premiums
- accounts
payable
Long-term liabilities can
include:
- Long-term
debt includes any interest and principal on bonds issued
- Pension
fund liability refers to the money a company is required to pay into its
employees' retirement accounts
- Deferred
tax liability is the amount of taxes that accrued but will not be
paid for another year. Besides timing, this figure reconciles differences
between requirements for financial reporting and the way tax is
assessed, such as depreciation calculations.
Why Is a Balance Sheet
Important?
The balance sheet is an essential tool used by executives, investors, analysts, and regulators to understand the current financial health of a business. It is generally used alongside the two other types of financial statements: the income statement and the cash flow statement.
Balance sheets allow
the user to get an at-a-glance view of the assets and liabilities of the
company. The balance sheet can help users answer questions such as whether the
company has a positive net worth, whether it has enough cash and short-term
assets to cover its obligations, and whether the company is highly indebted
relative to its peers.
Cash Book:- The word “cash” represents the monetary
instruments (currency etc.) and the word “book” represents the record available
in written format. Thus, a cash book can be defined as the record of business
transactions in a particular period.
In other words, a cash
book records all transactions of cash receipts and disbursements (includes both
bank deposits and withdrawals). Cash book is divided into two parts namely,
cash payments and cash receipts.
Transactions which are
not recorded or are excluded in cash book are as follows −
v Transactions related to bank (payments made through checks
in receiving or paid).
v Non-cash transactions.
v Discount making or discount received.
v Cash book satisfies objectives of journal and a
ledger
Cash book as journal
v Just like a journal, it records transactions in
chronological order (as it happens).
v Follows the same procedure in posting transactions to ledger
from cash book.
v Maintains special cash books for cash transactions.
v Records cash transactions according to debit and credit.
Cash book as ledger
v Same format as ledger.
v Follows the same T format as ledger.
v Cash book balances are transferred to trial balance.
v Serve purpose of cash account.
Types:- The cash books
can be classified primarily into four different types that are:
1. Simple Cash Books -
These are also
known as Single Column Cash Books. They are used to record the cash
transactions and the cash receipts (cash that comes in) are entered on the left
side while the cash payments are recorded on the right side. As all cash
transactions are recorded in one book, there is no need for a cash ledger
account.
2. Two Column Cash Books -
In a two-column
cash book, there is an additional column provided for recording the specific
discount entries which allow the discount transactions to be recorded in the
same cash book along with the cash transactions. This cash book is usually
maintained by organizations where it is a general practice to give or receive
discounts.
3. Three Column Cash Books -
As the name
suggests, three-column cash books have three columns; one for cash, one for the
discount, and the additional bank columns. For most of the organizations that
are now dealing with banking instruments like cheques or bills of exchange
along with cash, a bank column in the cash book makes simplified accounting
entries.



.png)



.png)



.png)
.jpeg)



























No comments:
Post a Comment